August 4, 2025
5 min read
Markus Kasanmascheff
Manus AI launches Wide Research, deploying 100+ AI agents in parallel to revolutionize large-scale research tasks and challenge single-agent models.
Manus AI Launches ‘Wide Research,’ Pitting 100-Agent Swarms Against ‘Deep Research‘ from Google and OpenAI
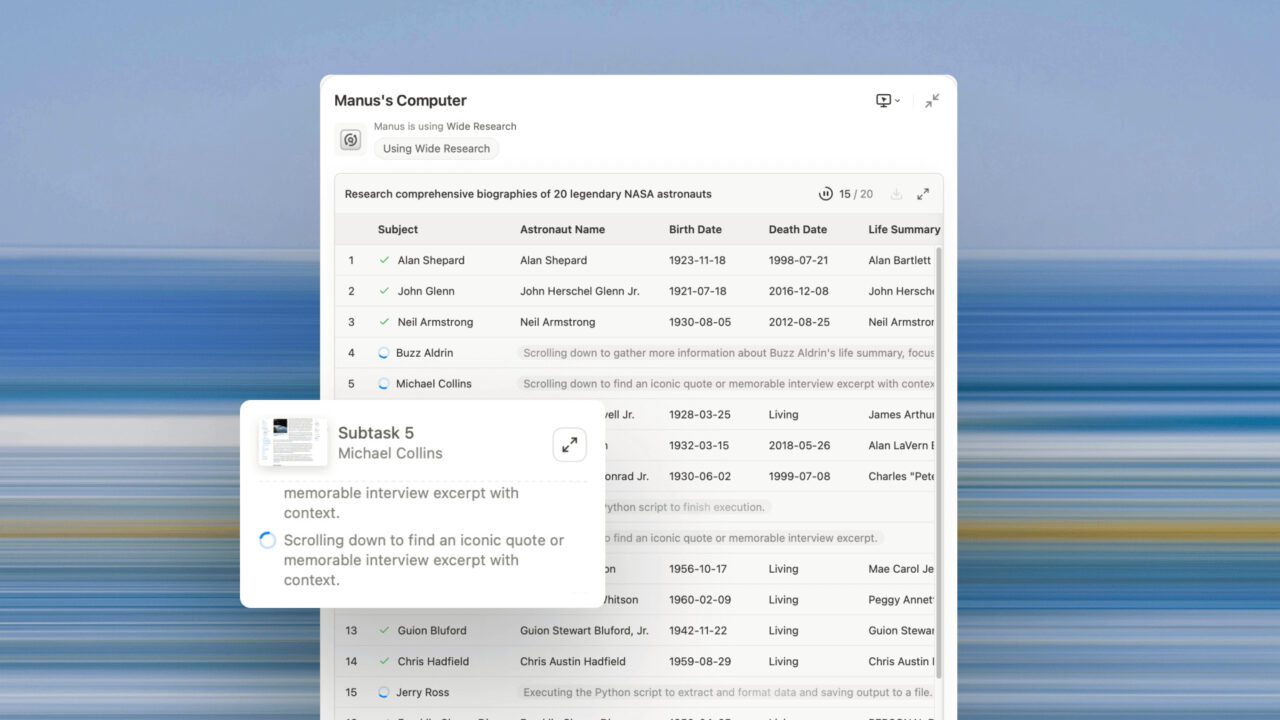
Singapore-based AI startup Manus has launched Wide Research, a novel feature for its agentic platform that deploys over 100 AI agents in parallel to tackle large-scale tasks. Announced on July 31, 2025, the system contrasts sharply with the “Deep Research” tools from competitors like OpenAI and Google. Manus frames the new capability as a personal supercomputing cluster, enabling users to orchestrate complex, high-volume research through natural language. The feature is now available to Manus Pro subscribers, with a gradual rollout planned for other tiers, marking a new approach to scaling AI-driven productivity.From Viral Sensation to Agentic Supercomputer
The launch builds on the significant buzz Manus generated in March 2025. Initially perceived as a Chinese AI venture, its parent company, Butterfly Effect, is now headquartered in Singapore, a strategic response to US-China tech tensions. The debut saw overwhelming demand, with partner Zhang Tao admitting, “we have completely underestimated the level of enthusiasm.” This history of high expectations sets the stage for Wide Research. Manus describes its core product not as an AI but as a “personal cloud computing platform.” In a recent blog post, the company explained its vision, stating, “AI can democratize that power. Behind every Manus session runs a dedicated cloud-based virtual machine, allowing users to orchestrate complex cloud workloads — simply by talking to an agent.” This architecture, where each agent is a Turing-complete virtual machine, is the foundation for its new feature.How ‘Wide Research’ Reimagines AI Collaboration
At its core, Wide Research is a system for parallel processing and agent-to-agent collaboration. Instead of one agent digging deep, Manus spins up a swarm to work in concert, effectively giving users control of a personal supercomputing cluster just by chatting. The goal is to scale the available compute for a single task by a factor of 100, transforming how complex problems are addressed. The practical applications demonstrate this breadth. In a demo shared by the company, Wide Research was tasked with comparing 100 different sneakers. It instantly deployed 100 concurrent subagents, each assigned to analyze one shoe, and returned a sortable matrix in both spreadsheet and webpage formats within minutes. Another example showcased its creative potential, with agents generating 50 distinct poster designs simultaneously, delivering the polished assets in a single ZIP file. The company emphasizes that “The key to Wide Research isn’t just having more agents — it’s how they collaborate.” This architectural choice is a critical differentiator. Unlike traditional multi-agent systems that rely on predefined, specialized roles like “manager” or “coder,” every subagent in Wide Research is a fully capable, general-purpose Manus instance running on its own virtual machine. This generality is what unlocks the system’s flexibility, ensuring that tasks are not constrained by rigid formats or domains.A Promising Architecture with Unproven Benefits
Wide Research is available now for users on the $199/month Pro plan, with access for Plus ($39/month) and Basic ($19/month) users to follow. However, the company has positioned the feature as experimental, and despite the ambitious claims, its practical benefits remain unproven. This cautious rollout reflects both the novelty of the architecture and the significant technical and regulatory hurdles the platform faces. Industry analysis has been quick to point out the lack of empirical evidence supporting the “wide” approach. As noted by VentureBeat, “while the feature showcases architectural ambition, its practical benefits over simpler methods remain unproven based on the information provided.” The company has not released performance benchmarks, direct comparisons to single-agent alternatives, or technical explanations detailing how subagents collaborate, how results are merged, or whether the system offers measurable advantages in speed, accuracy, or cost-efficiency. These are not trivial hurdles. The broader tech community has a mixed record with multi-agent systems, which are notoriously complex to develop and debug. Developers working with other platforms have reported challenges with high token consumption, slow performance, and a lack of visibility into execution. Early independent reviews of Manus itself noted performance inconsistencies, including generating simulated data or getting stuck in loops. These issues highlight the steep technical climb Manus faces in ensuring its agent swarms are both reliable and efficient. Furthermore, the company’s focus on autonomous operation has attracted significant regulatory scrutiny since its debut. Shortly after its initial launch, Tennessee Governor Bill Lee banned Manus from state networks, citing risks of “censorship, propaganda, and bias.” Alabama soon followed with a similar prohibition over security vulnerabilities. This government pushback reflects a global unease with fully autonomous systems that operate without a human-in-the-loop, a core design principle of the Manus platform. Ultimately, Wide Research represents a bold experiment in scaling AI. As the agentic AI market matures, the line between ambitious vision and practical utility becomes sharper. Its success will depend entirely on whether the architectural vision can overcome the well-documented challenges of multi-agent coordination and navigate a skeptical regulatory environment to deliver tangible advantages over simpler, more established methods.Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
About Wide Research and Manus AI
Q: What is Manus AI's Wide Research feature? A: Wide Research is a new feature from Manus AI that utilizes over 100 AI agents working in parallel to handle large-scale research tasks. It's designed to act like a personal supercomputing cluster controlled through natural language. Q: How does Wide Research differ from Google and OpenAI's research tools? A: While competitors like Google and OpenAI focus on "Deep Research" (often implying a single, in-depth agent), Manus AI's Wide Research employs a "swarm" or parallel processing approach with numerous agents working simultaneously to cover breadth rather than just depth. Q: What is the underlying architecture of Manus AI's platform that enables Wide Research? A: Manus describes its platform as a "personal cloud computing platform." Each AI agent runs on a dedicated, cloud-based virtual machine, making them Turing-complete and capable of complex, independent operations that can be orchestrated collaboratively. Q: What are some practical applications of Wide Research? A: Examples include rapidly comparing a large number of items (like 100 sneakers) by assigning each item to a separate agent, or generating multiple design variations (like 50 poster designs) concurrently. Q: What is the pricing for Wide Research access? A: As of its announcement, Wide Research is available to Manus Pro subscribers (priced at $199/month). Access for other tiers (Plus and Basic) is planned for a gradual rollout.Challenges and Future of Wide Research
Q: What are the main challenges or unproven aspects of Wide Research? A: Industry analysis indicates that the practical benefits of the "wide" approach over simpler methods remain unproven. The company has not yet released detailed performance benchmarks, direct comparisons, or technical explanations on how agent collaboration and result merging are handled. Q: What are the general challenges with multi-agent systems that Manus AI might face? A: Multi-agent systems are known for their complexity in development and debugging. Previous reviews of Manus have noted potential issues like performance inconsistencies, generating simulated data, and getting stuck in loops, which need to be overcome for the agent swarms to be reliable and efficient. Q: What regulatory hurdles does Manus AI face? A: The company's focus on autonomous operation has led to regulatory scrutiny. Some US states, like Tennessee and Alabama, have banned Manus from state networks due to concerns about censorship, propaganda, bias, and security vulnerabilities associated with fully autonomous systems.Crypto Market AI's Take
Manus AI's introduction of "Wide Research" signifies a fascinating pivot in how AI agents are being deployed for research and data analysis. By leveraging a swarm of over 100 agents, they are offering a different approach compared to the more singular, in-depth analysis often associated with major players like Google and OpenAI. This "wide" research methodology could be particularly powerful for tasks requiring broad coverage and parallel processing, such as market trend analysis or competitive landscape reviews within the cryptocurrency space. Our platform, Crypto Market AI, also utilizes advanced AI agents for cryptocurrency market analysis and trading. We focus on providing actionable insights and leveraging AI for efficient market navigation. The concept of orchestrating multiple AI agents to tackle complex tasks, as demonstrated by Manus AI, aligns with the growing trend of agentic AI. Understanding how these different approaches to AI agent deployment can benefit users, whether for broad research or for focused trading strategies, is key to leveraging AI effectively in the financial markets.More to Read:
- AI Agents: Capabilities, Risks, and Growing Role
- AI-Driven Crypto Trading Tools Reshape Market Strategies in 2025
- Understanding Cryptocurrency Ledgers: The Backbone of Blockchain
Source: Manus AI Launches ‘Wide Research,’ Pitting 100-Agent Swarms Against ‘Deep Research‘ from Google and OpenAI